The cockpit is a Red Hat Enterprise Linux web-based interface designed for managing and monitoring your local system, as well as Linux servers located in your network environment.
In RHEL 8 Cockpit is the default installation candidate we can just start the service and then can start the management of machines. For RHEL7 or Fedora based machines we can follow steps to install and configure the cockpit.
Following are the few features of cockpit.
- Managing services
- Managing user accounts
- Managing and monitoring system services
- Configuring network interfaces and firewall
- Reviewing system logs
- Managing virtual machines
- Creating diagnostic reports
- Setting kernel dump configuration
- Configuring SELinux
- Updating software
- Managing system subscriptions
Installation of cockpit package.
[root@rhel8 ~]# dnf install cockpit cockpit-dashboard -y
We need to enable the socket.
[root@rhel8 ~]# systemctl enable --now cockpit.socket
If firewall is running on the system then a rule should be added to allow access it.
[root@rhel8 ~]# firewall-cmd --add-service=cockpit --permanent
[root@rhel8 ~]# firewall-cmd --reload
Then we can access the cockpit console using the URL.
https://server.name.com:9090
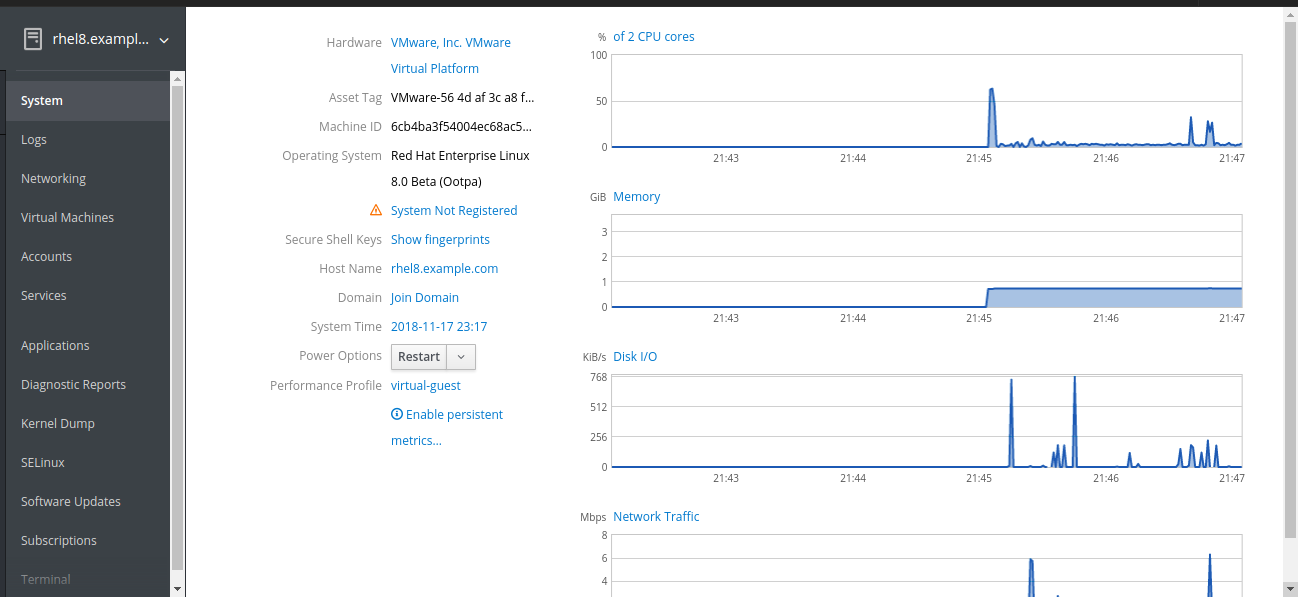
ADD REMOTE SYSTEMS
On remote machine, we need to install the cockpit package.
[root@centos7 ~]# yum install cockpit
Go to url https://cockpit-server:9090/dashboard
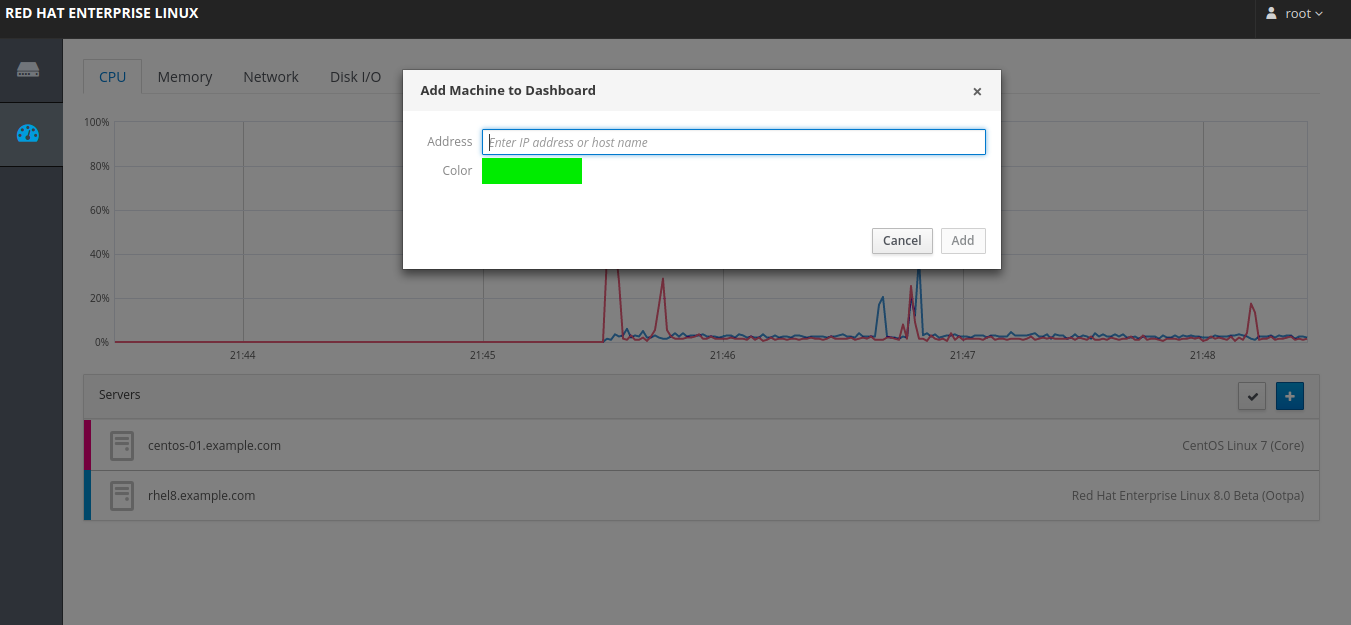
click on + botton and add the remote server with IP address and username and password.
Once the server added then we would the list of servers just click on the server we can manage all the things on the server from GUI console.
Comments
Post a Comment